Major sporting events like the World Cup, Super Bowl, and Wimbledon attract millions, even billions, of viewers. Argentina’s shootout win over France in the final game of the Qatar 2022 World Cup reached a global audience of 1.5 billion viewers. And the Olympics, starting later this month in Paris, is the biggest of them all—with the 2020 Tokyo Olympics having attracted a worldwide audience of over 3 billion viewers.
These events are also prime opportunities for cybercriminals. Over the past decade, the number of cyberattacks targeting major events has surged, increasing from 212 million documented attacks at the London 2012 Games to a staggering 4.4 billion at the Tokyo 2020 Games. These attacks often have direct financial motives, such as scams, digital fraud, or the acquisition of valuable data from attendees, viewers, and sponsors. In their excitement, eager fans often overlook potential risks when purchasing tickets, arranging accommodations, or buying memorabilia, making them easy targets for cybercriminals.
Others, desperate to view specific events, are enticed by malicious websites offering free access, only to have their devices compromised or personal data stolen. And with the world’s media focused on the event, criminals with a political agenda are looking for a large audience for their message by disrupting a significant site or knocking critical services offline.
Threat Actors Targeting the Paris 2024 Games
According to new FortiGuard Labs analysis based on threat intelligence provided by FortiRecon, this year’s Olympics has been a target for a growing number of cybercriminals for over a year. Using publicly available information and proprietary analysis, this report provides a comprehensive view of planned attacks, such as third-party breaches, infostealers, phishing, and malware, including ransomware.
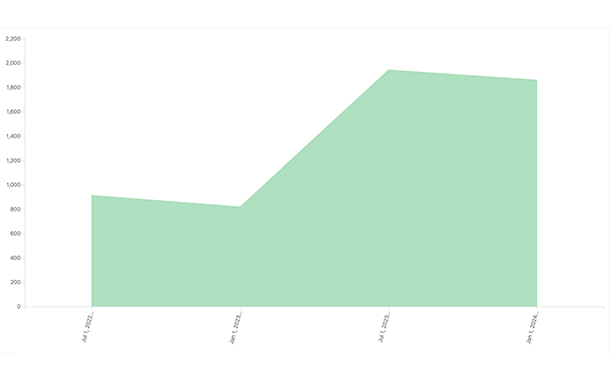
FortiGuard Labs has observed a significant increase in resources being gathered leading up to the Paris Olympic Games, especially those targeting French-speaking users, French government agencies and businesses, and French infrastructure providers.
Notably, since the second half of 2023, we saw a surge in darknet activity targeting France. This 80% to 90% increase has remained consistent across 2H 2023 and 1H 2024. The prevalence and sophistication of these threats are a testament to the planning and execution of cybercriminals, with the dark web serving as a hub for their activities.
Conclusion
In addition to celebrating athleticism and sportsmanship, the Paris Olympics 2024 is a high-stakes target for cyberthreats, drawing attention from cybercriminals, hacktivists, and state-sponsored actors. Cybercriminals are leveraging phishing scams and fraudulent schemes to exploit unsuspecting participants and spectators.
Fake ticketing platforms, fraudulent merchandise, and identity theft tactics threaten financial loss and undermine public trust in event-related transactions. Further, due to France’s political stances and international influence, the Paris Olympics 2024 is also a prime target for politically motivated groups.
We anticipate that hacktivist groups will focus on entities associated with the Paris Olympics to disrupt the event, targeting infrastructure, media channels, and affiliated organizations to disrupt event proceedings, undermine credibility, and amplify their messages on a global stage.